《css层叠上下文(stacking context)和层叠顺序(stacking order)》
# 层叠上下文(stacking context)
对于stacking context,在MDN中的描述是
层叠上下文是HTML元素的三维概念,这些HTML元素在一条假想的相对于面向(电脑屏幕的)视窗或者网页的用户的 z 轴上延伸,HTML 元素依据其自身属性按照优先级顺序占用层叠上下文的空间。 z轴即用户与屏幕间看不见的垂直线。
# 层叠水平(stacking level)
层叠水平顺序决定了同一个层叠上下文中元素在z轴上的显示顺序
# 层叠顺序(stacking order)
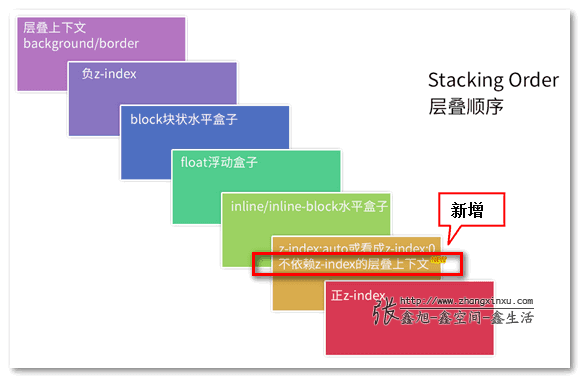
不过上面图示的说法有一些不准确,按照 W3官方 的说法,准确的 7 层为:
- the background and borders of the element forming the stacking context.
- the child stacking contexts with negative stack levels (most negative first).
- the in-flow, non-inline-level, non-positioned descendants.
- the non-positioned floats.
- the in-flow, inline-level, non-positioned descendants, including inline tables and inline blocks.
- the child stacking contexts with stack level 0 and the positioned descendants with stack level 0.
- the child stacking contexts with positive stack levels (least positive first).
翻译过来是:
- 形成层叠上下文环境的元素的背景与边框
- 拥有负 z-index 的子堆叠上下文元素 (负的越高越堆叠层级越低)
- 正常流式布局,非 inline-block,无 position 定位(static除外)的子元素
- 无 position 定位(static除外)的 float 浮动元素
- 正常流式布局, inline-block元素,无 position 定位(static除外)的子元素(包括 display:table 和 display:inline )
- 拥有 z-index:0 的子堆叠上下文元素
- 拥有正 z-index: 的子堆叠上下文元素(正的越低越堆叠层级越低)
# 层叠准则
- 层叠上下文的水平比普通元素高。
- 当元素的层叠水平一致、层叠顺序相同的时候,在DOM流中处于后面的元素会覆盖前面的元素。
- 层叠上下文内部嵌套的子元素均受父元素影响。
- 层叠上下文不会影响兄弟元素,只会影响后代元素。
- 在同一层叠水平上时,有明显的z-index值,则值越大,谁在上。
- 使用了css3属性的时候,层叠顺序是跟z-index:auto/z-index:0是一样的,当他们发生层叠的时候,遵循的是“后来居上”准则。
注意:
- 普通元素的层叠水平优先由层叠上下文决定,因此,层叠水平的比较只有在当前层叠上下文元素中才有意义。
- 如果父元素没有创建层叠上下文的时候,子元素没有受父元素的限制,父子元素是处于同一层叠水平,比较时需要按上面的7层进行比较。
- 只设置了position:absolute/relative是不会创建层叠上下文的,此时的div是一个普通元素。
- position:fixed在chrome等较高级浏览器中,就算设置为z-index:auto也会创建层叠上下文。
# 层叠上下文的创建
以下摘自 MDN:
- 根元素 (HTML)
- z-index为数值的定位元素
- css3的属性
- 一个 z-index 值不为 "auto"的 flex 项目 (flex item),其子元素为层叠上下文元素
- opacity 属性值小于 1 的元素
- transform 属性值不为 "none"的元素
- mix-blend-mode 属性值不为 "normal"的元素
- filter值不为“none”的元素
- perspective值不为“none”的元素
- isolation 属性被设置为 "isolate"的元素
- position: fixed
- 在 will-change 中指定了任意 CSS 属性,即便你没有直接指定这些属性的值
- -webkit-overflow-scrolling 属性被设置 "touch"的元素
# demo演示
本文案例可以在 css-stacking-context 中下载查看。
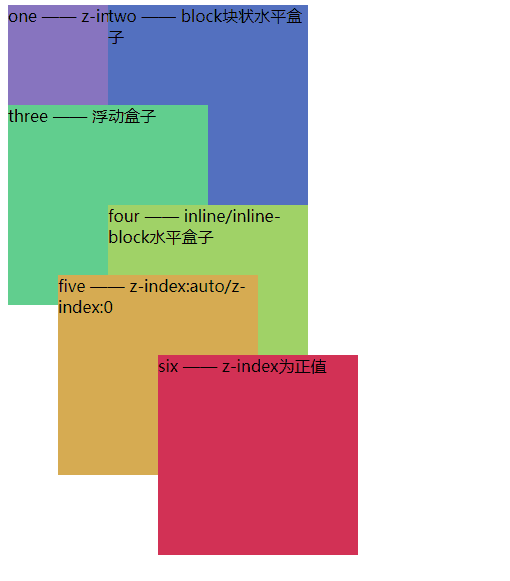
- 7阶层叠顺序
html
<div class="one">one —— z-index为负值</div>
<div class="two">two —— block块状水平盒子</div>
<div class="three">three —— 浮动盒子</div>
<div class="four">four —— inline/inline-block水平盒子</div>
<div class="five">five —— z-index:auto/z-index:0</div>
<div class="six">six —— z-index为正值</div>
2
3
4
5
6
css
.one,.two,.three,.four,.five,.six{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
.one{
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
background: #8874c1;
}
.two{
background: #4f6fc1;
margin-left: 100px;
}
.three{
float: left;
background: #51cd8d;
margin-top: -100px;
}
.four{
display: inline-block;
background: #9cd262;
margin-left: -100px;
}
.five{
position: absolute;
background: #d9ac4c;
margin-top: -130px;
margin-left: 50px;
}
.six{
position: absolute;
z-index: 1;
background: #d93953;
margin-top: -50px;
margin-left: 150px;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
效果图:注意inline/inline-block的元素层级是高于float元素的,因为inline/inline-block是内容展示,所以层级比较高
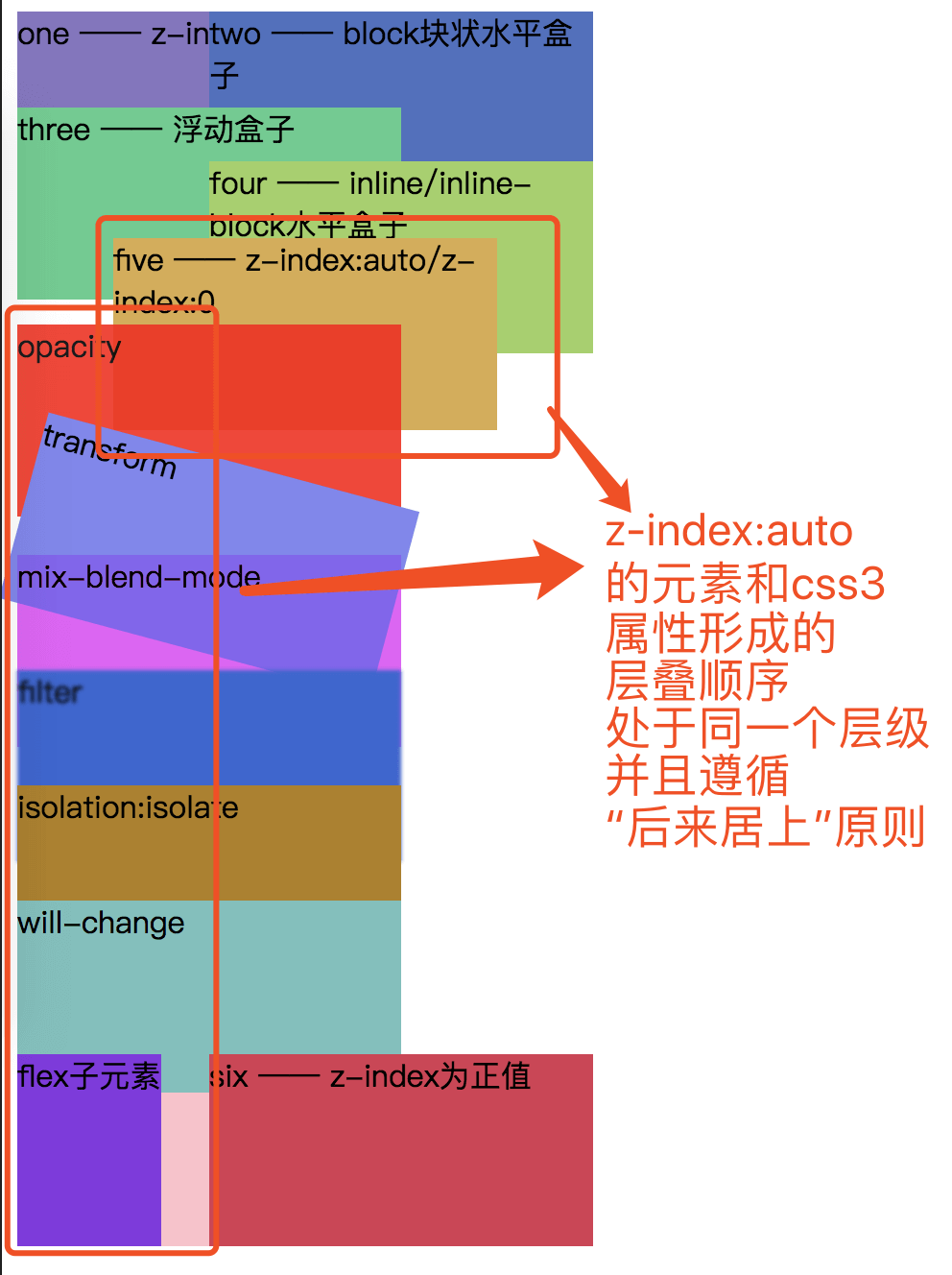
- 当使用了css3属性之后的7阶层叠顺序
html
<div class="one">one —— z-index为负值</div>
<div class="two">two —— block块状水平盒子</div>
<div class="three">three —— 浮动盒子</div>
<div class="four">four —— inline/inline-block水平盒子</div>
<div class="five">five —— z-index:auto/z-index:0</div>
<div class="five-2">opacity</div>
<div class="five-3">transform</div>
<div class="five-4">mix-blend-mode</div>
<div class="five-5">filter</div>
<div class="five-6">isolation:isolate</div>
<div class="five-7">will-change</div>
<div class="five-1">
<div class="five-1-sub">flex子元素</div>
</div>
<div class="six">six —— z-index为正值</div>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
css
.one, .two, .three,
.four, .five,.six {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
}
.one {
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
background: #8874c1;
}
.two {
background: #4f6fc1;
margin-left: 100px;
}
.three {
float: left;
background: #51cd8d;
margin-top: -50px;
}
.four {
display: inline-block;
background: #9cd262;
margin-left: -100px;
margin-top: -30px;
}
.five {
position: absolute;
background: #d9ac4c;
margin-top: -60px;
margin-left: 50px;
}
.six {
position: absolute;
z-index: 1;
background: #d93953;
margin-top: -100px;
margin-left: 100px;
}
.five-1,.five-2, .five-3,
.five-4,.five-5,.five-6,
.five-7 {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
}
.five-1 {
display: flex;
margin-top: -20px;
background: pink;
}
.five-1-sub {
background: blueviolet;
z-index: 1;
}
.five-2{
opacity: 0.9;
background: red;
margin-top: -15px;
}
.five-3 {
transform: rotate(15deg);
background: #8484f1;
margin-top: -30px;
}
.five-4 {
mix-blend-mode: darken;
background: #ec57f9;
margin-top: -50px;
}
.five-5 {
filter: blur(1px);
background: #3a64d4;
margin-top: -40px;
}
.five-6 {
isolation: isolate;
background: #b18017;
margin-top: -40px;
}
.five-7 {
background: #73c1bc;
will-change: transform;
margin-top: -40px;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
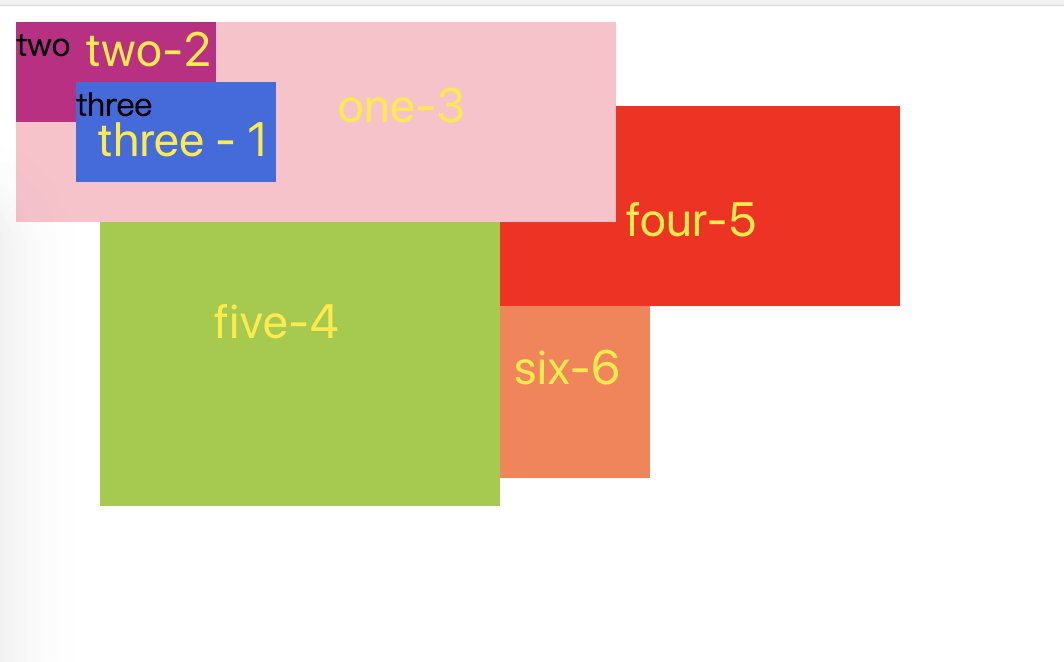
效果图:可以明显看出,css3属性造成的层叠上下文跟z-index:auto同一个层级,并且遵循“后来居上”原则
- 当元素的层叠水平一致、层叠顺序相同的时候,在DOM流中处于后面的元素会覆盖前面的元素。 html
<div class="one">
one
<div class="one-sub">
one-sub
</div>
</div>
<div class="two">
two
</div>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
css
.one,.two,.one-sub{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
.one{
position: absolute;
z-index: 5;
background: red;
}
.one-sub{
position: absolute;
z-index: 100; // 设多高都没用
background: purple;
}
.two{
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
z-index: 5;
background: orange;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
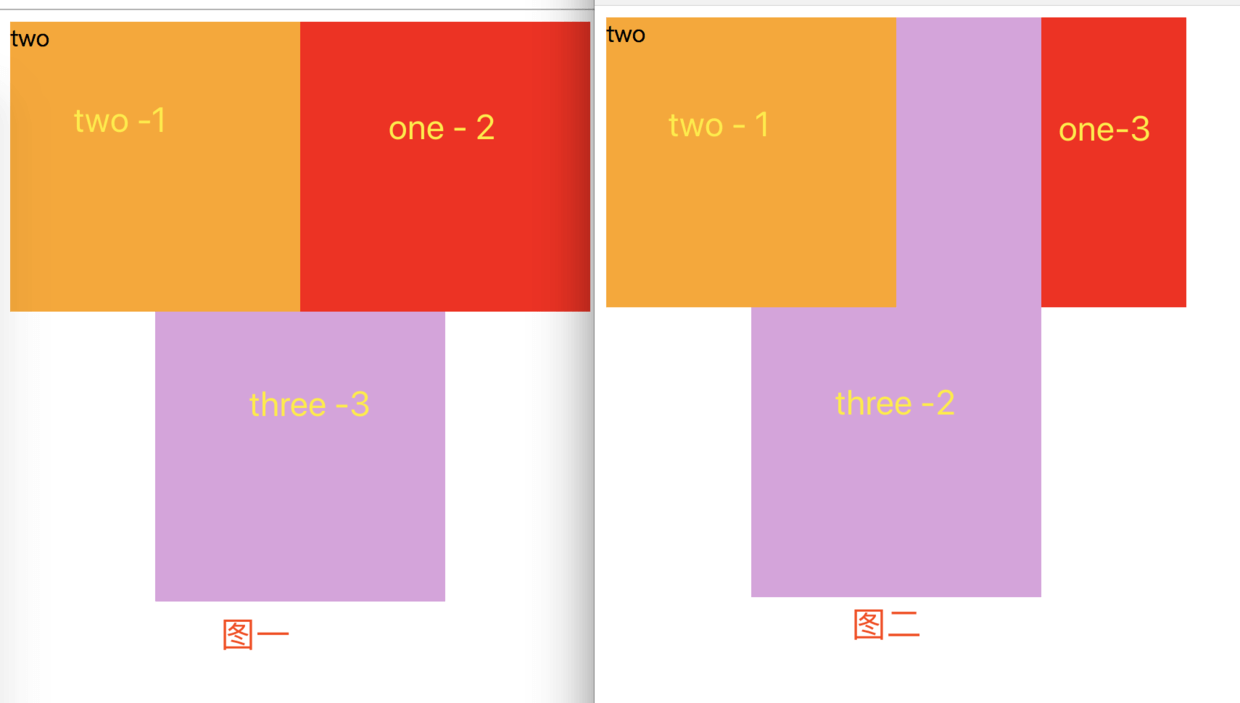
效果图: 可以看到同层级的 two 是覆盖了 one 的,而one中的子元素one-sub无论z-index层级设置多高,都是无法覆盖 two 的

- 处于层叠上下文内部嵌套的子元素均受父元素影响。 html
<div class="one">
<div class="two">two</div>
<div class="three">three</div>
</div>
2
3
4
5
css
.one{
position: absolute;
background: red;
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
/* z-index: 100; */ // 不加效果为图一,加了效果为图二
}
.two{
position: absolute;
z-index: 2;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: orange;
}
.three{
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
width: 200px;
height: 400px;
left: 100px;
background: plum;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
效果图:
- 图一:one仅仅设置了position:absolute/relative; 没有设置z-index值的时候,z-index:默认为auto;此时不会创建层叠上下文。所以此时one是普通元素,比它的子元素three的层级要高
- 图二:当one设置了层级之后,此时one已经创建了层叠上下文,此时one里面的子元素受制one,意思就是,one的子元素层级永远比one要高。
注意:chrome等较高级浏览器中,position:fixed;就算设置为z-index:auto也会创建层叠上下文。所以图一的代码,将absolute改成fixed,也会出现图二的效果。
# 一道面试题
PS:附赠一道笔试题目,可以试一下是否能答对。
题目:写出从上到下的层叠顺序,例如.one .two .four ... 答案:见文末。
html
<div class="one">
<div class="two"></div>
<div class="three"></div>
</div>
<div class="four">
<div class="five"></div>
<div class="six"></div>
</div>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
css
.one{
position:relative;
z-index:2;
.two{
z-index: 6;
}
.three{
position: absolute;
z-index: 5;
}
}
.four{
position:absolute;
.five{}
.six{
position: absolute;
left:0;
top:0;
z-index: -1;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
参考自:
深入理解CSS中的层叠上下文和层叠顺序 层叠上下文【stacking context】与层叠顺序【stacking order】 层叠顺序与堆栈上下文知多少
答案:three two one five four six
解析:
- one 和 four是同级元素,由于 one是z-index数值为正的定位元素,所以one的层级比four高
- 既然one已经创建了层叠上下文,那么它的子元素就会受限于它,接下来分析一下里面的子元素。two只是设置了z-index,并没有创建层叠上下文,所以是普通元素,three是z-index为正值的定位元素,所以three层级比two高。目前得出的结论是three、 two、 one。
- 接下来看four,因为four只设置了定位,没有设置z-index,所以默认是auto,所以four是没有创建层叠上下文的,four是普通元素,也就是block块级水平盒子的层级。
- five没有设置任何样式,那么他是处于block块级水平盒子的层级,基于后来居上的原则,five层级要比four要高,而six是z-index为负值的定位元素,所以是处于z-index负值的层级,所以得出的结论就是five 、four、 six。
- 进行一下排序就是three、 two、 one 、five、 four 、six。
# css3属性介绍
1. mix-blend-mode 混合模式 - 用css就能实现ps中的混合模式
html
<div class="img1">
<h2>变化看这里变化看这里变化看这里变化看这里</h2>
<img src="https://ss0.bdstatic.com/70cFuHSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=1436948145,4270509323&fm=200&gp=0.jpg">
</div>
2
3
4
css
.img1{
position: relative;
}
h2{
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
mix-blend-mode: soft-light; // 有多种值可选
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9

具体可看以下介绍: mix-blend-mode MDN CSS3混合模式mix-blend-mode/background-blend-mode简介
2. isolation — 隔离mix-blend-mode元素的混合
- isolation属性定义该元素是否必须创建一个新的层叠上下文stacking context,从而阻断混合模式。
- 只要元素可以创建层叠上下文,就可以阻断mix-blend-mode
具体可看以下介绍: isolation MDN 理解CSS3 isolation: isolate的表现和作用
3. filter — 滤镜效果
html
<div class="img1">
<img src="https://ss0.bdstatic.com/70cFuHSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=1436948145,4270509323&fm=200&gp=0.jpg">
</div>
2
3
css
.img1{
position: relative;
filter: blur(5px); // 有多种值可选
}
2
3
4
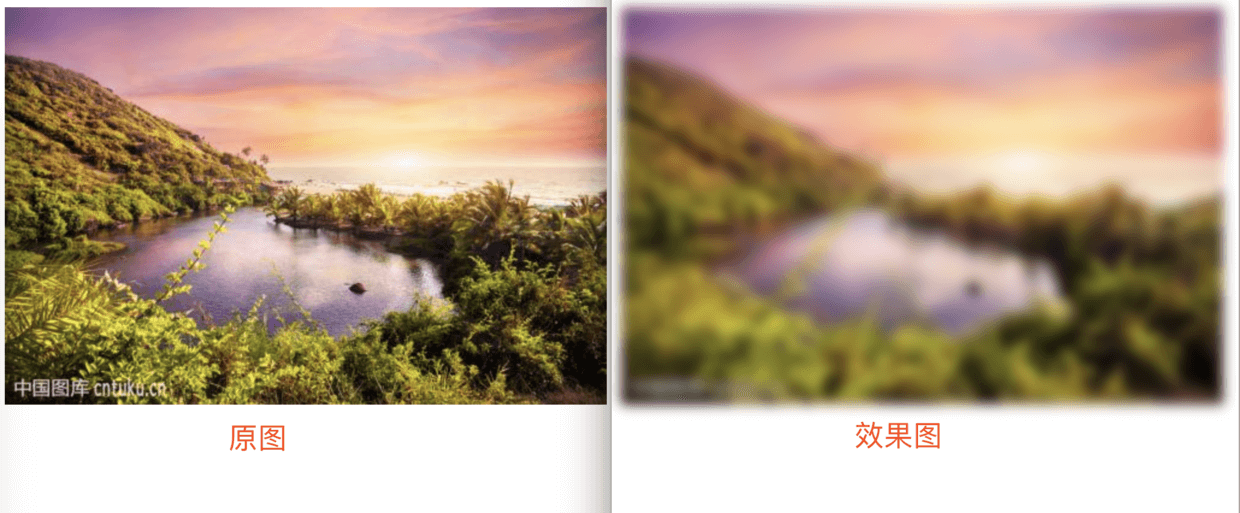

具体可看以下介绍: filter MDN
- will-change
- -webkit-overflow-scrolling
# 最后
欢迎提出意见和建议。
