《遍历数组的12种方法》
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
1
# 1. for
普通版
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length;i++ ){
//代码
}
1
2
3
2
3
优化版
// 使用临时变量,将长度缓存起来,避免重复获取数组长度,当数组较大时优化效果才会比较明显。
for(let i = 0, len=arr.length; i < len; i++) {
//代码
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
for 循环和 for-in 能正确响应break、continue和return语句,但forEach不行。具体可看return 、break和continue的区别和作用
# 2. foreach
接收一个回调函数作为参数, 该回调接收3个参数。
- tem:每个元素
- index:元素数组下标
- arr:数组本身
注意:
- foreach() 不会对空数组进行检测。
arr.forEach((item,index,arr)=>{
//代码
})
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
# 3. map
map的用法和forEach差不多。但 map 有返回值
注意:
- map() 不会对空数组进行检测。
- map() 不会改变原始数组。
const brr= arr.map((item,index,arr)=>{
//代码
return item * 2;
})
console.log(brr) // [2, 4, 6]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 4. for-of
只有可迭代对象(iterator)才能使用。(包括 Array,Map,Set,String,TypedArray,arguments 对象等等)。
普通对象是不能使用的。
for(let item of arr){
//代码
}
1
2
3
2
3
# 5. filter
接受一个回调函数作为参数,返回值是一个新数组
注意:
- filter() 不会对空数组进行检测。
- filter() 不会改变原始数组。
const arr = [
{name:'tony',age:'20'},
{name:'jack',age:"30"}
]
const brr = arr.filter(item=>{
return item.age > 20;
})
console.log(brr) // [{name:'jack',age:"30"}]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 6. every
every()是对数组中的每一项运行给定函数。如果该函数对每一项返回true,则返回true(全部符合条件),否则返回 false
注意:
- every() 不会对空数组进行检测。
- every() 不会改变原始数组。
const arr= [50, 6, 70, 80];
const flag = arr.every((item,index,arr)=>{
return item > 50; //每一项数据都要大于50
})
console.log(flag) // false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 7. some
some()是对数组中每一项运行指定函数,如果该函数对任一项返回true,则返回true。(只要有一个符合),否则返回false
注意:
- some() 不会对空数组进行检测。
- some() 不会改变原始数组。
const arr= [50, 6, 70, 80];
const flag = arr.some((item,index,arr)=>{
return item > 50; //只要有一项数据都要大于50
})
console.log(flag) // true
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
# 8. reduce
reduce()方法接收一个函数作为累加器,数组中每个值(从左往右)开始缩减,最终计算为一个值。
reduce(fun, initialValue)
注意:
- reduce() 对于空数组是不会执行回调函数的。
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
arr.reduce((initialValue, currentValue, index, arr) => {
console.log(initialValue) // 第一次循环 initialValue = 1
return initialValue + currentValue; // 6
})
arr.reduce((initialValue, currentValue, index, arr) => {
console.log(initialValue) // 第一次循环 initialValue = 10
return initialValue + currentValue; // 16
}, 10)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 9. reduceRight
reduceRight()方法的功能和reduce()功能是一样的,不同的是reduceRight()从数组的末尾向前将数组中的数组项做累加。
- reduceRight() 对于空数组是不会执行回调函数的。
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
arr.reduceRight((initialValue, currentValue, index, arr) => {
console.log(initialValue) // 第一次循环 initialValue = 3
return initialValue + currentValue; // 6
})
arr.reduceRight((initialValue, currentValue, index, arr) => {
console.log(initialValue) // 第一次循环 initialValue = 10
return initialValue + currentValue; // 16
}, 10)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 10. find
返回数组中符合测试函数条件的第一个元素。否则返回undefined
注意:
- find() 对于空数组,函数是不会执行的。
- find() 并没有改变数组的原始值。
const arr = [
{name:'tony',age:'20'},
{name:'jack',age:"30"}
]
const result = arr.find(item=>{
return item.name === 'jack';
})
console.log(result) // {name:'jack',age:"30"}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 11. findIndex
返回传入一个测试函数条件的第一个元素的位置,没有则返回 -1。
注意:
- findIndex() 对于空数组,函数是不会执行的。
- findIndex() 并没有改变数组的原始值。
const arr = [
{name:'tony1',age:'20'},
{name:'tony2',age:'20'},
{name:'tony3',age:'20'},
{name:'jack',age:"30"},
]
const result = arr.find(item=>{
return item.name === 'jack';
})
console.log(result) // 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 12. keys、values、entries
它们都返回一个遍历器对象,可以用for...of循环进行遍历。
- keys() —— 返回元素索引
- values() —— 返回元素本身
- entries() —— 返回元素和索引
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c']
for (let index of arr.keys()) {
console.log(index);
}
// 0
// 1
// 2
for (let elem of arr.values()) {
console.log(elem); // a b c
}
// a
// b
// c
for (let [index, elem] of arr.entries()) {
console.log(index, elem);
}
// 0 "a"
// 1 "b"
// 2 "c"
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 13. 比较
# jsperf
性能检测工具:jsperf
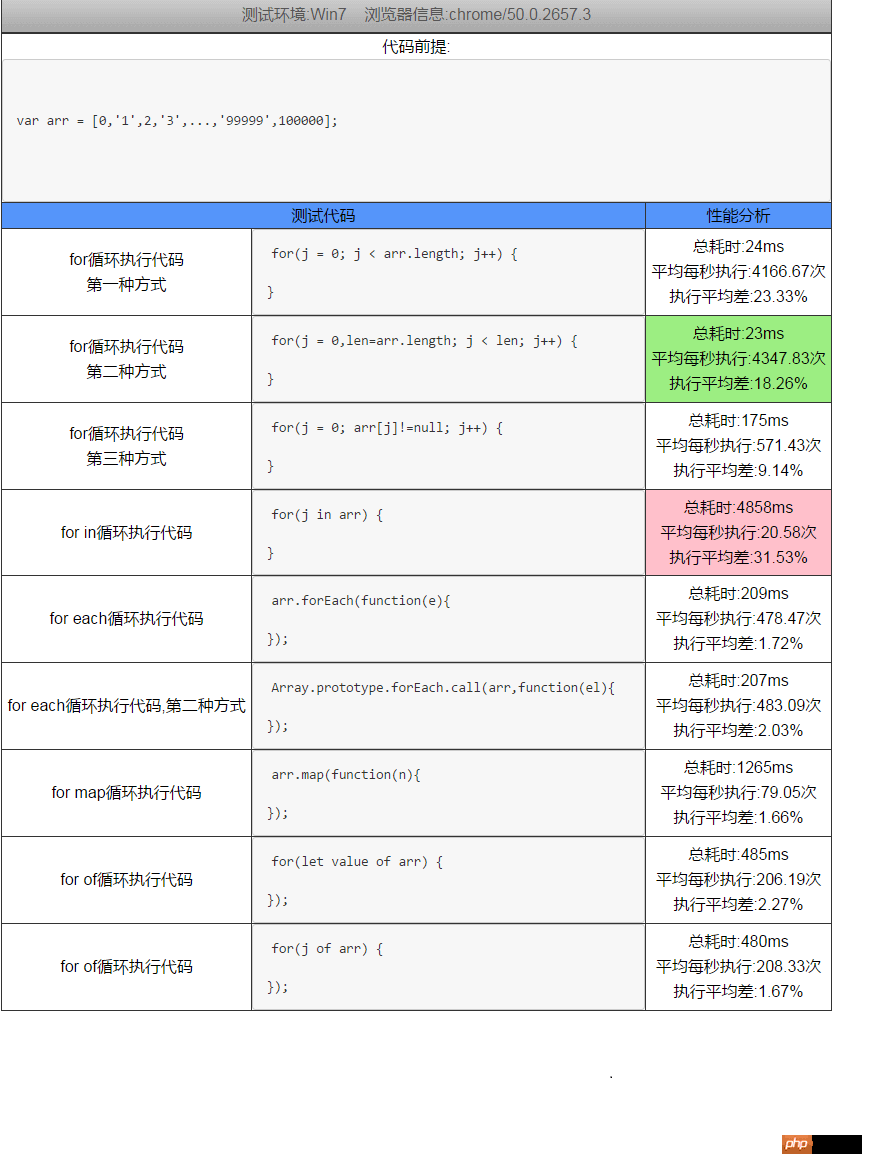
# 手动检测
也可以使用 console.time(ID); 计时器手动检测,不同机器不同浏览器版本有差异。
var arr = Object.keys(Array.apply(null, { length: 100000 })).map(function(
item
) {
return +item;
});
console.time("timer1");
for(let i = 0, len = arr.length; i < len;i++ ){
//代码
}
console.timeEnd("timer2");
// timer2: 1.718017578125ms
console.time("timer2");
arr.forEach((item,index,arr)=>{
//代码
});
console.timeEnd("timer2");
// timer3: 1.708984375ms
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
